Table Of Content
- Relations with Other Patterns — TL;DR;
- Step 1: Define the Handler Interface
- Structural Design Patterns
- ATM Money Dispenser Using Chain of Responsibility Design Pattern
- How does error handling work in the Chain of Responsibility pattern?
- Chain of Responsibility Design Pattern in C#
- Chain of Responsibility Pattern Examples in JDK
- Explore design patterns using Python with code examples to solve common software challenges. …

If the Team Leader has authority to take action on that request, he will process the and give the result (approved/ denied). If he does not have the authority, he will pass it to the next person (Project Leader) in the chain. Please create a class file named Handler.cs and copy and paste the following code. Here, you can see that we created one variable of type Handler (i.e., NextHandler), and this variable will hold the reference of the Next Handler. If this is not clear now, don’t worry; you will understand the need for this variable after a while. The concrete handler classes will implement this abstract DispatchNote() method.
Relations with Other Patterns — TL;DR;
This current implementation necessitates passing the Request object through all the filters. However, what if we want to halt the propagation through the filter chain when a specific condition is met? A common example is during a web request, where we don’t want to continue processing if authentication fails.
Step 1: Define the Handler Interface
The association of corporate social responsibility and sustainable consumption and production patterns: The mediating ... - ScienceDirect.com
The association of corporate social responsibility and sustainable consumption and production patterns: The mediating ....
Posted: Tue, 15 Aug 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
While the example below doesn’t solve all the CoR issues, it shows how the pattern can be easily restructured and adapted to different logic. If you are interested, you can use the following GitHub link to see my complete implementation of Chain of Responsibility pattern. As you can see on the UML diagram, it has 3 type of components named as, Client, Handler, and Concrete-Handler. When a user points the mouse cursor at an element and presses the F1 key, the application detects the component under the pointer and sends it a help request.
Structural Design Patterns
First, create a class file named TeamLeader.cs and copy and paste the following code. As you can see here, first, we created one variable, i.e., MAX_LEAVES_CAN_APPROVE, to hold the maximum leave value the Team Leader can approve. This class implements the EmployeeLeaveHandler abstract class and provides the implementation for the ApplyLeave() method. As part of the ApplyLeave method, we check whether the Team Leader can approve the number of leaves the employee applies.
ATM Money Dispenser Using Chain of Responsibility Design Pattern
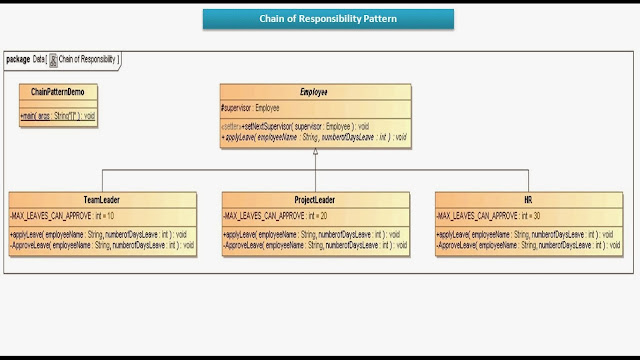
When we insert our ATM card into the machine and initiate a transaction, the ATM system employs the Chain of Responsibility pattern to handle our request, ultimately providing us with the requested cash. Now we have to implement a separate class for each request approver (Concrete Handlers) in this company. As a result, I have created a separate class for Team Leader, Project Leader, HR, and Manager. All these classes extend the “LeaveHandler” class and implement the “applyLeave” method within them. The Cocoa and Cocoa Touch frameworks, used for OS X and iOS applications respectively, actively use the chain-of-responsibility pattern for handling events. Objects that participate in the chain are called responder objects, inheriting from the NSResponder (OS X)/UIResponder (iOS) class.
How does error handling work in the Chain of Responsibility pattern?
Javatpoint provides tutorials with examples, code snippets, and practical insights, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced developers. Now we will define the ATM withdrawal process in order to define the use of paper currency dispenser. We will arrange the paper currency dispensers in higher to lower face value order. About the Author Marcin Zarębski is an experienced back-end developer, specializing in. He has amazing skills in building complex backend solutions and infrastructure. Marcin is also interested in space exploration and the role of computer science in it.
Best of 2023: Top 9 Microservices Design Patterns - Cloud Native Now
Best of 2023: Top 9 Microservices Design Patterns.
Posted: Wed, 03 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
The application can attempt to authenticate a user to the system whenever it receives a request that contains the user’s credentials. However, if those credentials aren’t correct and authentication fails, there’s no reason to proceed with any other checks. The request is sent by the client, who then forwards it to the chain’s first handler.
In this example, the Chain of Responsibility pattern is responsible for displaying contextual help information for active GUI elements. He keeps quoting lengthy excerpts from the manual, refusing to listen to your comments. After hearing the phrase “have you tried turning the computer off and on again? ” for the 10th time, you demand to be connected to a proper engineer.
This pattern encourages loose coupling between sender and receiver, providing freedom in how the request is handled. Unlike other behavioral design patterns, the Chain of Responsibility pattern creates a linear sequence or a chain of receiver objects for a request. Each receiver in the chain either handles the request or passes it to the next receiver. The primary advantage of using the Chain of Responsibility design pattern is that it decouples the sender and receiver of a request. This means that the sender doesn’t need to know the details of who handles the request, or how it’s handled.

If the processor is not able to process anything, it just forwards the same request to the next chain. Each linked handler has a field for storing a reference to the next handler in the chain. In addition to processing a request, handlers pass the request further along the chain. The request travels along the chain until all handlers have had a chance to process it. ➡ One of the behavioral design patterns.➡ Its main goal is to decouple the behavior of an object from its state by modeling the behavior into an abst... In chain of responsibility, sender sends a request to a chain of objects.
The request bubbles up through all the element’s containers until it reaches the element that’s capable of displaying the help information. Eventually, the operator passes your call to one of the engineers, who had probably longed for a live human chat for hours as he sat in his lonely server room in the dark basement of some office building. The engineer tells you where to download proper drivers for your new hardware and how to install them on Linux.
If a particular object cannot handle that request, it will pass the request to the next object in that chain. In simple words, we can say that the chain of responsibility design pattern creates a chain of receiver objects for a given request. In this design pattern, normally, each receiver contains a reference to the next receiver. If one receiver cannot handle the request, it passes the same request to the next receiver, and so on.
Each stage has a specific responsibility, and the order in which these stages are executed is crucial. This is precisely where the Chain of Responsibility Design Pattern comes into play. I will pass various level of support requests down the chain and they will be handled by correct level. Chain of Responsibility allows a number of classes to attempt to handle a request, independently of any other object along the chain.
While it has advantages like flexibility and decoupling, be mindful of potential downsides, such as the risk of unhandled requests and slight performance overhead. Ultimately, the Chain of Responsibility pattern empowers you to design elegant and modular solutions to complex problems in the world of software engineering. Design patterns are indispensable tools in the software engineer’s toolbox. The Chain of Responsibility pattern is a powerful choice when you need to create a flexible and extensible processing chain. By understanding its principles and applying them in Python, you can improve the maintainability and scalability of your software systems. Imagine having a toolbox of tried-and-true solutions readily available.

No comments:
Post a Comment